top of page

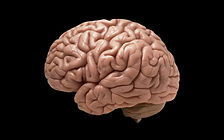
The brain is a highly complex organ that serves as the command center of the central nervous system. It controls nearly all functions of the body, including thoughts, emotions, memory, speech, movement, and physiological processes. Here’s a simplified explanation of how the brain works:
1. Neurons and Synapses: The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells called neurons.
Neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals at junctions
called synapses.
2. Electrical Signals: Neurons generate electrical impulses, known as action potentials, which travel along their axons (long projections) to transmit information to other neurons or to muscles and glands.
3. Chemical Signaling : When an action potential reaches the end of an axon (axon terminal), it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synapse. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that bind to receptors on neighboring neurons, transmitting signals across the synapse.
4. Brain Regions: Different regions of the brain have specialized functions. For example, the cerebral cortex is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as reasoning, language, and sensory perception, while the cerebellum controls coordination and balance.
5. Integration of Information:The brain integrates sensory information received from the body and external environment to produce appropriate responses. This process involves complex networks of interconnected neurons that work together to process, interpret, and store information.
6. Plasticity and Learning: The brain exhibits neuroplasticity, the ability to reorganize and form new connections in response to learning and experience. This allows for adaptation and development throughout life.
7. Control of Body Functions:The brain also regulates involuntary functions such as heart rate, breathing, and digestion through the autonomic nervous system, which includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
In summary, the brain functions through the coordinated activity of neurons and synapses, allowing for the processing and integration of information, control of bodily functions, and the generation of thoughts, emotions, and behaviors that define human experience.

Scan for AR view
bottom of page